What Are the Different Types of Belt Drives? A Complete Guide to Pros, Cons & Applications
Overwhelmed by belt drive options? Choosing the wrong one leads to inefficiency and downtime. This guide simplifies belt drives, helping you pick the right one.
Belt drives are mechanical systems that use belts to transmit power between shafts. Different types, like V-belts, timing belts, and flat belts, offer unique advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications.
You’ve probably seen belt drives in action, whether in your car engine or in factory machinery. But do you know the differences between them? It’s important to pick the right one. The correct belt drive can make a big difference in performance and efficiency.
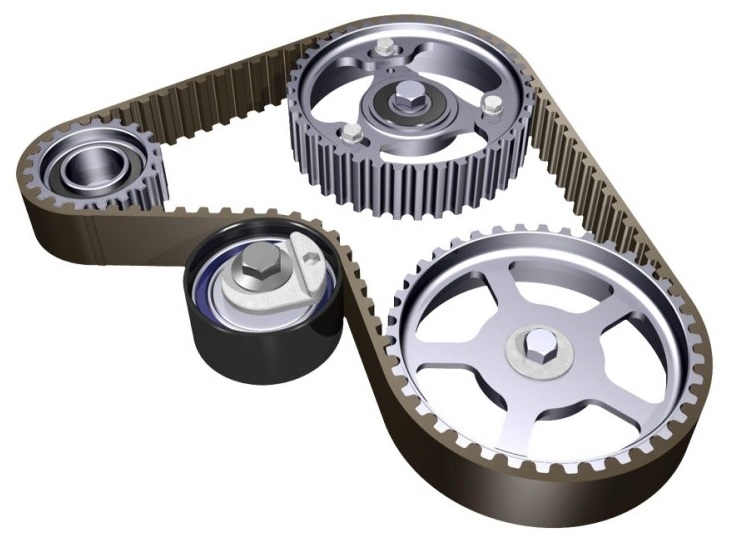
Now, you might be thinking, "Belts are just belts, right?" Wrong! The world of belt drives is more complex than you think. So, let’s get into the specifics. I will help you understand the core types. I will also guide you on where they are best used.
What Are the Core Types of Belt Drives? From Flat Belts to Timing Belts—A Technical Breakdown
Confused about the different kinds of belt drives? Not knowing the types can lead to poor equipment choices. Learn the core types with their technical details.
The main types of belt drives include flat belts, V-belts, round belts, timing belts, and multi-rib belts. Each type varies in design, materials, and how they transmit power, making them suitable for different applications.
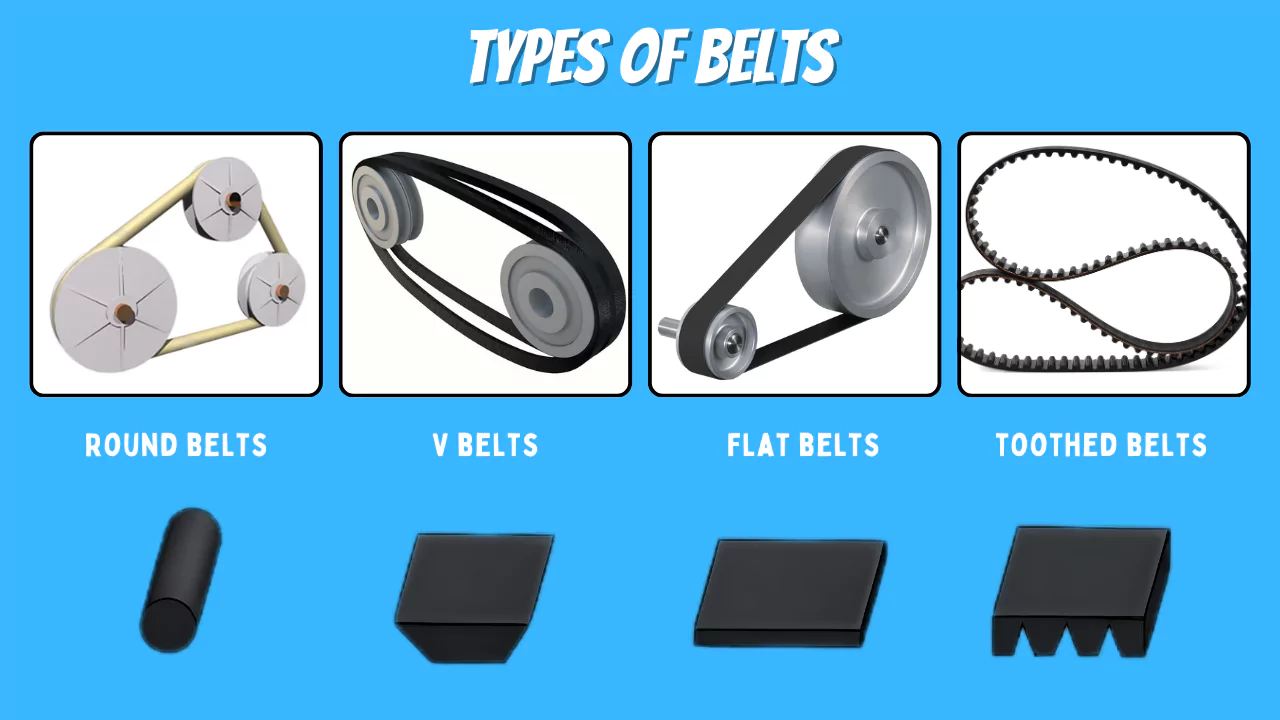
Let’s dive into each type of belt drive. Flat belts are the oldest type. They are simple and work well at high speeds. However, they don’t transmit as much power as other types and can slip easily. V-belts are the most common type. They use a V-shaped belt that fits into a V-shaped groove on the pulley. This increases friction and allows for better power transmission compared to flat belts. Round belts are circular in cross-section and are often used in light-duty applications like sewing machines and small conveyors. Timing belts, also known as synchronous belts, have teeth that mesh with corresponding grooves on the pulleys. This provides a positive, non-slip drive. These are used in applications requiring precise timing, such as automotive engines. Multi-rib belts, also known as poly-V belts, have multiple ribs running lengthwise. This increases the contact area and allows for high-power transmission in compact designs. I remember touring a factory where they used a mix of belt drives. Flat belts were on the older machines, V-belts were everywhere, and timing belts controlled critical processes. Understanding these differences is key to choosing the right belt drive.
| Belt Type | Cross-Section | Power Transmission | Speed | Application Examples |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flat Belt | Rectangular | Low | High | Old Machinery, Conveyors |
| V-Belt | V-Shaped | Medium | Medium | Automotive, Industrial |
| Round Belt | Circular | Low | Low | Sewing Machines, Light Duty |
| Timing Belt | Toothed | High | Medium | Automotive Engines, Robotics |
| Multi-Rib Belt | Multi-Ribbed | High | High | Automotive, Appliances |
How Do Belt Drives Differ in Performance? Weighing the Pros & Cons of Each Category
Unsure which belt drive offers the best performance? Choosing poorly can lead to frequent repairs and lost productivity.Compare the pros and cons of each type for optimal performance.
Belt drives differ in efficiency, power transmission, speed capabilities, noise levels, and maintenance requirements. Flat belts are simple but slip, while timing belts are precise but costly. V-belts balance cost and performance.
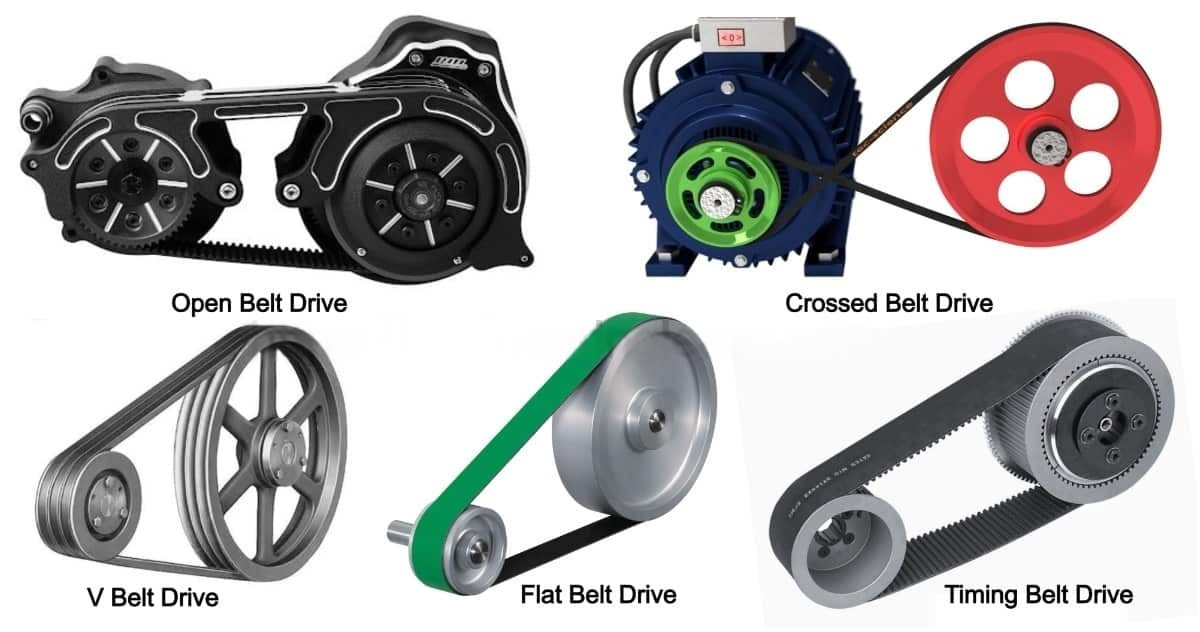

When it comes to performance, each belt drive has its strengths and weaknesses. Flat belts are simple and inexpensive but suffer from low efficiency due to slippage. They also require frequent adjustments. V-belts offer a good balance between cost and performance. They transmit more power than flat belts and are relatively easy to maintain. Round belts are quiet and smooth-running but are limited to light-duty applications. Timing belts provide the highest level of precision and power transmission, but they are more expensive and require careful alignment. Multi-rib belts combine high-power capacity with flexibility. However, they can be more complex to install. I have seen companies struggle with belt drive performance. A printing company was using flat belts on a high-speed press. They had constant problems with slippage and inconsistent print quality. Switching to timing belts solved the problem. This improved the precision and reliability of their operation.
| Belt Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Flat Belt | Simple, Inexpensive | Low Efficiency, Slippage |
| V-Belt | Good Balance, Easy Maintenance | Medium Efficiency |
| Round Belt | Quiet, Smooth | Low Power Capacity |
| Timing Belt | High Precision, No Slippage | Expensive, Requires Alignment |
| Multi-Rib Belt | High Power, Flexible | Complex Installation |
Where Are Different Belt Drives Used? Real-World Applications Across Industries
Curious about where specific belt drives are used? Applying the wrong belt drive can lead to operational inefficiencies. Discover real-world applications across industries.
Flat belts are in older machinery and conveyors. V-belts are in automotive engines and industrial equipment. Timing belts are in automotive engines and robotics. Multi-rib belts are in car engines and appliances.
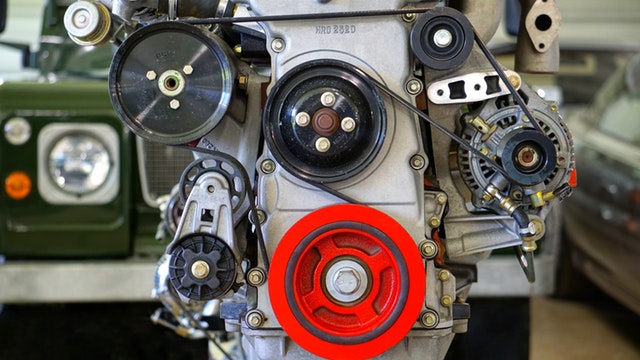
Different belt drives are used in various industries based on their unique characteristics. Flat belts were commonly used in older factory machinery and agricultural equipment. Today, they are still found in some conveyor systems and woodworking machines. V-belts are the workhorses of power transmission. They are used in automotive engines, industrial machinery, HVAC systems, and agricultural equipment. Timing belts are essential in applications that require precise synchronization. This includes automotive engines (for timing the camshaft and crankshaft), robotics, and printing presses. Multi-rib belts are popular in modern automotive engines to drive multiple accessories. They are also used in appliances like washing machines and dryers. I once visited a textile mill that used a complex network of belt drives. Flat belts powered the older looms, V-belts drove the newer spinning machines, and timing belts controlled the precision knitting equipment. Understanding these applications helps you appreciate the versatility of belt drives.
| Belt Type | Industry | Application Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Flat Belt | Manufacturing | Conveyors, Woodworking Machines |
| V-Belt | Automotive | Engine Accessories, Power Steering |
| V-Belt | Industrial | Pumps, Compressors, Fans |
| Timing Belt | Automotive | Camshaft, Crankshaft Synchronization |
| Timing Belt | Robotics | Precise Movement Control |
| Multi-Rib Belt | Automotive | Alternator, Air Conditioning Compressor |
| Multi-Rib Belt | Appliances | Washing Machines, Dryers |
How to Choose the Right Belt Drive? Key Factors for Optimal Selection
Overwhelmed by the factors in choosing a belt drive? Making the wrong choice leads to inefficiency and potential failures. Consider these key factors for the best selection.
Choosing the right belt drive involves considering power requirements, speed ratios, operating environment, space constraints, and cost. Match these factors to the pros and cons of each belt type.

Selecting the right belt drive can seem daunting. It becomes easier if you break it down into key factors. First, determine the power requirements of your application. How much horsepower needs to be transmitted? This will help you narrow down the types of belts that can handle the load. Next, consider the speed ratio between the driving and driven shafts. Do you need to increase or decrease the speed? This will affect the pulley sizes and belt length. The operating environment is also important. Will the belt be exposed to extreme temperatures, chemicals, or abrasive materials? Choose a belt material that can withstand these conditions. Space constraints can also play a role. Do you have limited space for the belt drive system? Multi-rib belts and V-belts are often a good choice for compact designs. Finally, consider the cost. Balance the initial cost of the belt drive system with its long-term operating costs, such as maintenance and replacement. I always advise my clients to think long-term. A slightly more expensive belt drive that lasts longer and requires less maintenance can save money in the long run.
| Factor | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Power Requirements | Horsepower, Torque |
| Speed Ratio | Input Speed, Output Speed |
| Operating Environment | Temperature, Chemicals, Abrasive Materials |
| Space Constraints | Available Space, Pulley Sizes |
| Cost | Initial Cost, Maintenance Cost, Replacement Cost |
Conclusion
Choosing the right belt drive depends on the application. Consider power, speed, and environment. This ensures optimal performance and efficiency.
SANTE offers a variety of Drive Belts, including Wrapped V-Belts, Cogged V-Belts, and Timing Belts. We meet the needs of many applications. To learn more about SANTE’s extensive selection of Drive Belts, contact us today!