What Are Engine Belts? A Guide to Types, Functions, Maintenance & Replacement
Engine belts are often overlooked. Ignoring them can lead to costly repairs and breakdowns. Understand engine belts to ensure your vehicle’s smooth operation.
Engine belts are crucial components that drive auxiliary systems. They include Timing belts, Serpentine belts/Poly v-belts, and V-belts, each serving specific roles in the engine’s operation.
Many car problems start with neglected engine belts. They power essential systems. Knowing their types and functions can save you from unexpected breakdowns.
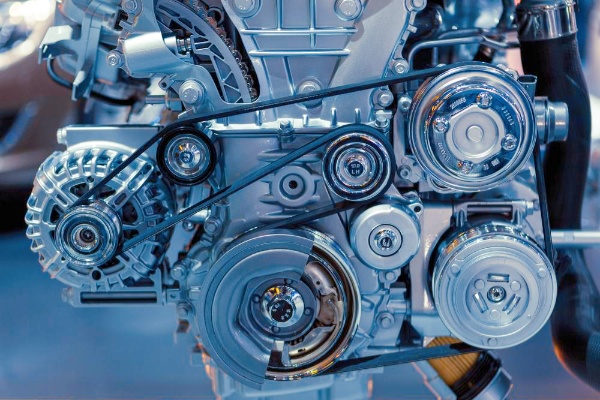
I remember facing a sudden breakdown due to a snapped serpentine belt. It taught me the importance of regular checks and understanding belt types. Let’s explore these different belts further.
What Are the Main Types of Engine Belts and How Do They Differ?
Confused by different engine belts? This leads to poor maintenance and potential damage. Learn the main kinds and their differences.
Engine belts include Timing belts, Serpentine belts/Poly V-belts, and V-belts. Timing belts synchronize engine parts, serpentine belts power multiple accessories, and V-belts are used in older engines for individual components.
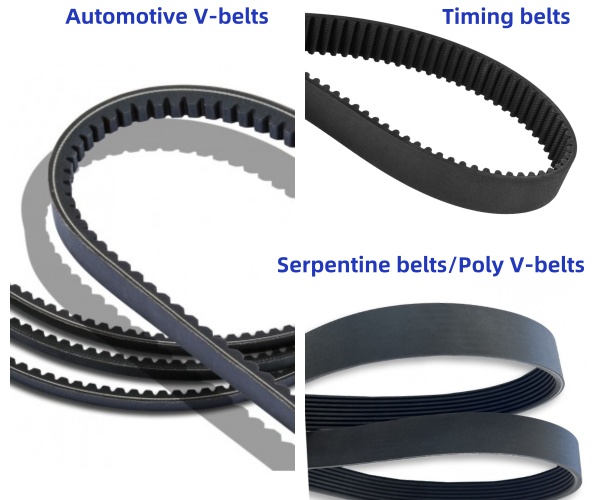
Engine belts are categorized by their functions and designs:
-
Timing Belts: Made from rubber with reinforced fibers, timing belts synchronize the rotation of the crankshaft and camshaft. This ensures valves open and close at the right times. Critical in maintaining engine efficiency and avoiding catastrophic damage. Timing belts are usually found in light-duty applications.
-
Serpentine Belts: These are long, single belts, driving multiple peripheral devices such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. Made from durable materials, their minimal maintenance needs make them a favorite in modern engines.
-
V-Belts: Present mostly in older engines, where several V-belts would drive individual components. They offer good grip, but require regular tension adjustments and often have shorter lifespans due to higher friction.
Every mechanical system where belts exist has unique requirements. I have personally seen older engines benefit immensely from timely V-belt replacements. Meanwhile, modern engines thrive on serpentine belts that minimize maintenance.
| Belt Type | Function | Material | Application Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Timing Belt | Synchronizes Engine Parts | CR/HNBR | Light-Duty Engines |
| Serpentine Belt | Powers Multiple Accessories | CR/EPDM | Modern Cars |
| V-Belt | Drives Individual Components | CR/EPDM | Older Engines |
How Do Engine Belts Work and Why Are They So Important?
Unclear on how engine belts function? Ignorance leads to inefficient performance. Learn how they work.
Engine belts transfer rotational energy from the engine to various components. Their role in maintaining proper timing and accessory functions is crucial for engine health and efficiency.
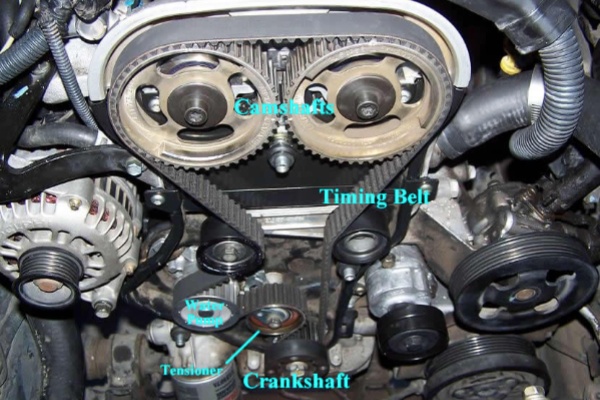
The primary function of engine belts is to communicate mechanical power across systems. Without engine belts, none of your car’s accessories would work. Here’s how they contribute to vehicle operation:
-
Timing Belts: Responsible for ensuring the engine’s valves open at precise intervals. They keep the engine running smoothly and prevent piston-valve collisions that could severely damage the engine.
-
Serpentine Belts: Are routed around several pulleys. This configuration lets one belt drive multiple devices, simplifying design, lowering maintenance demands, and improving efficiency. They reduce potential wear points, making them more reliable over extended periods.
-
V-Belts: Offer direct power transmission. While they provide excellent grip, individual belts drive separate accessories, leading to more maintenance needs.
The importance of engine belts cannot be overstated. A poorly functioning timing or serpentine belt can lead to decreased fuel efficiency and increased emissions. Experiencing engine failure from a neglected belt has driven home the point about regular maintenance.
What Are the Signs of Engine Belt Wear or Failure?
Wondering about belt wear indicators. Unrecognized wear leads to sudden failures and costly fixes. Recognize the signs early.
Signs of engine belt wear include squealing noises, visible cracks, abrasions, or misalignment. Regular inspection helps identify these symptoms before they lead to belt failure.
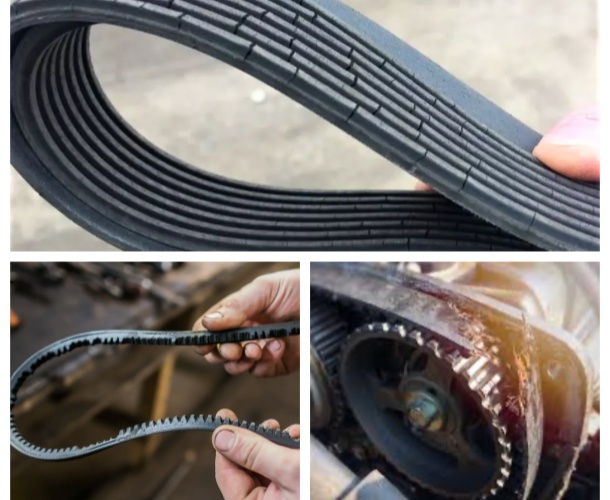

Recognizing the symptoms of wear or failure is essential in preventing unexpected breakdowns:
-
Squealing Noises: Often heard during start-up when the belt slips due to poor tension or wear. This is a common sign of aging belts in need of replacement.
-
Visible Cracks and Wear: Cracks in the belt’s rubber surface reveal its deterioration. Examine your engine belts regularly for abrasions or fraying fibers.
-
Misalignment: Regularly aligned belts run smoothly; however, if shifting occurs, it’s a sign of immediate attention needed.
Knowing these signs can save you from potential trouble. I’ve seen squealing belts lead to alternator issues due to unchecked wear. Regular checks and timely replacements are vital.
When and How Should You Replace or Maintain Engine Belts?
Overwhelmed by belt maintenance schedules? Improper maintenance results in failures. Follow regular replacement timelines and proper checks.
Timing belts should be replaced every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, serpentine belts checked every 30,000 miles, and adjustments made when wear is evident. Regular checks prevent unexpected failures.

Different belts have different lifespans. Here’s how to maintain them:
-
Timing Belts: Replace according to your manufacturer’s recommended mileage. Regularly inspect for wear to avoid engine damage.
-
Serpentine Belts: Check every 30,000 miles. They’re crucial for multiple systems, and early detection of wear extends their life.
-
V-Belts: Require regular tension adjustments. Inspect frequently for any gaps, looseness, or visible wear.
Regular engine checks are essential to catch early signs of wear. I maintain a schedule for routine belt inspections, ensuring smooth engine performance. Following the manufacturer’s guide on belt maintenance prevents failures and costly repairs.
Conclusion
Engine belts, including timing, serpentine, and V-belts, are vital for smooth operation. Understanding their types and functions ensures proper maintenance and prevents failures.
SANTE offers a diverse selection of engine belts, including Automotive Timing belts, Serpentine Belts/Ribbed Poly V-Belts, and Automotive V-belts. Contact [email protected] for belt solutions tailored to your needs.


