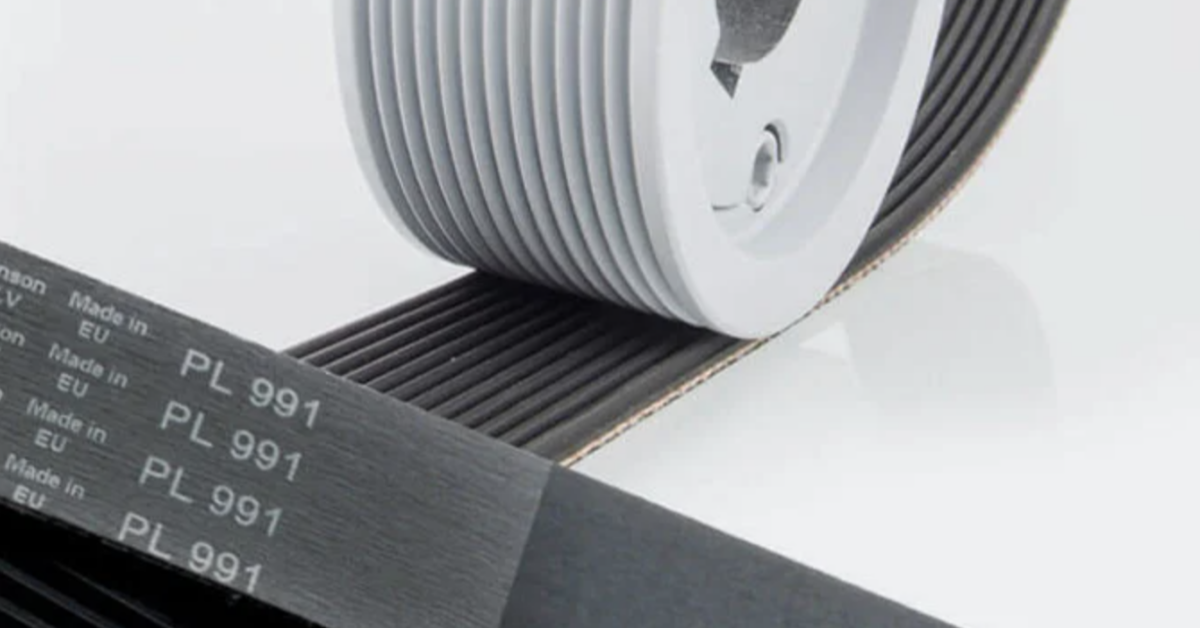
What do the belt section designations mean for ribbed V-belts?
Confused by the codes on ribbed V-belts? Choosing the wrong belt can cause slippage or damage. This guide simplifies ribbed V-belt markings for accurate selection.
The belt section designations on ribbed V-belts tell you about the belt’s dimensions, specifically the rib pitch (distance between ribs) and the belt’s overall profile. Understanding these codes ensures you select the right belt for your system.
You may have seen codes like “PK,” “PJ,” or “PH” on ribbed V-belts and wondered what they mean. Well, these designations are important. They help you match the right belt to your machinery. Let’s break it down.
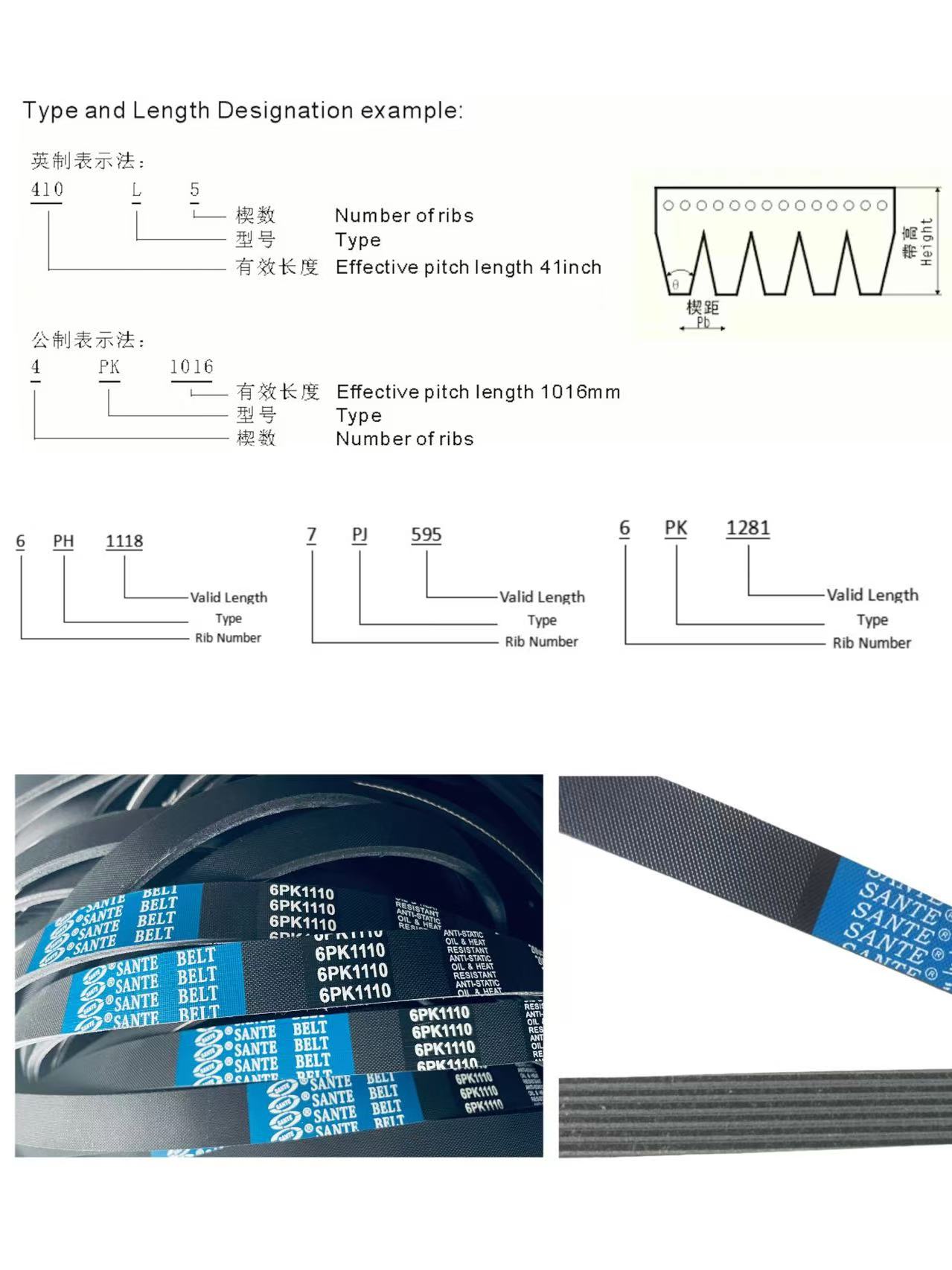
It’s easy to feel lost when you see all those letters and numbers. But don’t worry! I’ll explain what each part means. This way, you can confidently choose the correct ribbed V-belt every time.
What is a ribbed v-belt?
Unfamiliar with ribbed V-belts? Using the wrong belt type leads to inefficiency and potential damage. Learn what ribbed V-belts are and where they excel.
A ribbed V-belt, also known as a poly-V belt, has multiple V-shaped ribs running lengthwise. These ribs fit into matching grooves on the pulley, distributing the drive force evenly across the entire belt width.

Ribbed V-belts are different from traditional V-belts. A traditional V-belt has a single V-shape that fits into a groove. Ribbed V-belts have multiple ribs. This design offers several advantages. The multiple ribs increase the contact area between the belt and the pulley. This improves grip and reduces slippage. It also allows the belt to transmit more power than a traditional V-belt of the same width. Ribbed V-belts are commonly used in automotive, industrial, and appliance applications. They are great for serpentine drives where the belt needs to drive multiple components like alternators, power steering pumps, and air conditioning compressors. They are also suitable for high-speed applications. Their design minimizes vibration and noise. I have seen firsthand how ribbed V-belts can improve the efficiency and reliability of various machines.
| Feature | Traditional V-Belt | Ribbed V-Belt |
|---|---|---|
| Ribs | Single V-Shape | Multiple Longitudinal |
| Contact Area | Smaller | Larger |
| Power Capacity | Lower | Higher |
| Application | Simpler Drives | Serpentine Drives |
What are the different types of ribbed v-belts?
Overwhelmed by the variety of ribbed V-belts available? Choosing the wrong type can lead to poor performance and belt failure. Identify the different types of ribbed V-belts to make the right choice.
Ribbed V-belts come in several types, including PH, PJ, PK, PL, and PM. Each type has a different rib pitch, meaning the distance between each rib varies. The right type depends on the specific requirements of your drive system.
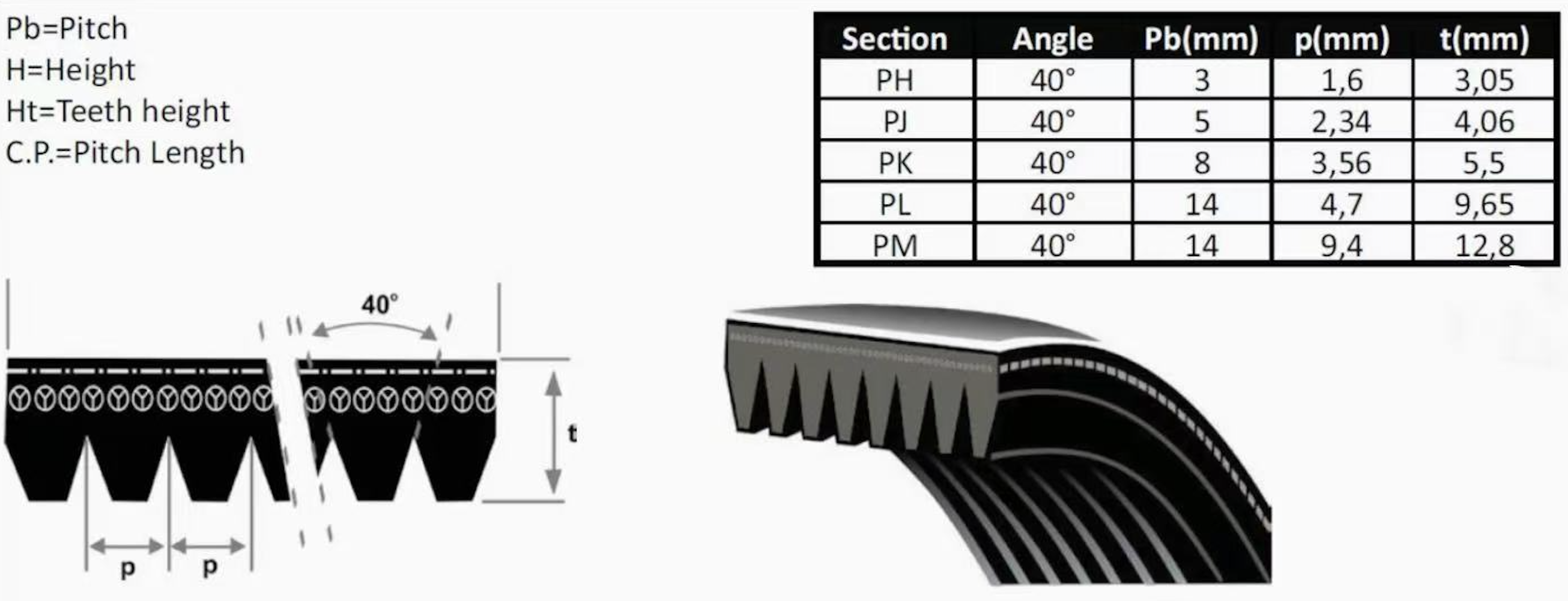
The different types of ribbed V-belts are designated by letters. Each letter corresponds to a specific rib pitch. The rib pitch is the distance between the center of one rib to the center of the next rib. Here’s a quick rundown:
- PH: Used in small appliances and some industrial applications.
- PJ: Common in appliances and HVAC systems.
- PK: Widely used in automotive applications.
- PL: Suitable for heavier industrial machinery.
- PM: Used in very heavy-duty applications.
The choice depends on the power requirements, pulley sizes, and operating speeds of your system. For example, PK belts are popular in cars because they handle the high speeds and varying loads well. PJ belts are often found in washing machines and dryers due to their ability to handle the bending and twisting in those machines. I remember a project where we had to replace the belts on a large industrial fan. We originally used PJ belts, but they kept failing due to the high torque. Switching to PL belts solved the problem. They provide the extra strength and durability needed for that application.
| Belt Type | Rib Pitch (mm) | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| PH | 1.6 | Small Appliances, Light Industrial |
| PJ | 2.34 | Appliances, HVAC |
| PK | 3.56 | Automotive |
| PL | 4.7 | Heavy Industrial Machinery |
| PM | 9.56 | Very Heavy-Duty Industrial Equipment |
How are ribbed belts measured?
Not sure how to measure ribbed belts for replacement? Inaccurate measurements lead to ordering the wrong size and wasting time. Follow these steps to measure ribbed belts accurately.
Ribbed belts are measured by their effective length, which is the total length of the belt when installed. You also need to know the belt’s section (PH, PJ, PK, etc.) to ensure the rib pitch matches your pulleys.
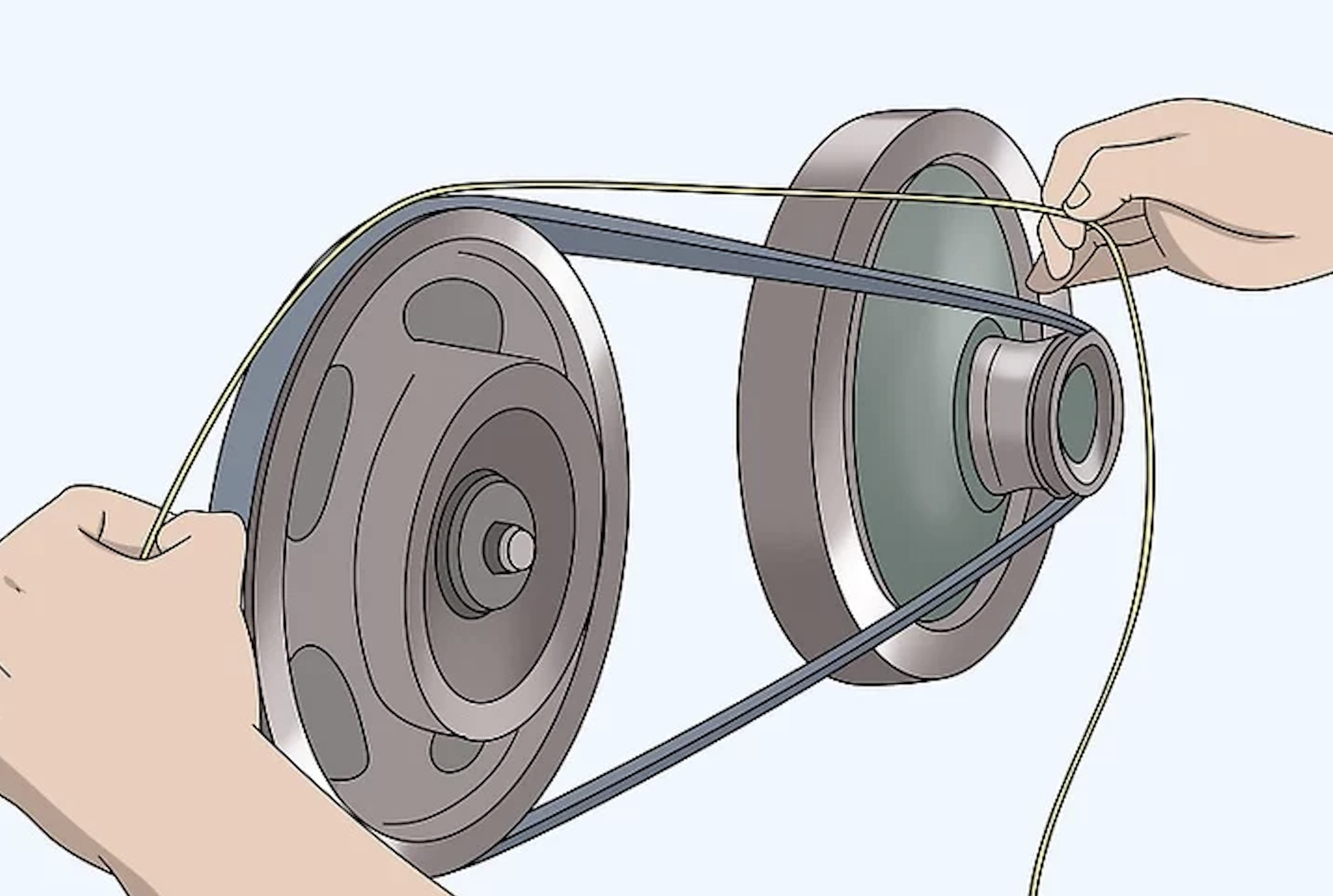
Measuring a ribbed belt involves a few key steps. First, identify the belt section (PH, PJ, PK, etc.). This is usually printed on the belt itself. If the marking is worn off, you can measure the rib pitch using a caliper or a ruler. Then, measure the effective length of the belt. The easiest way to do this is to use a flexible measuring tape. Wrap the tape around the outside of the belt, following its contours. This will give you the effective length. You can also use a belt measuring tool, which is a device designed specifically for this purpose. If you don’t have the old belt, you can measure the distance around the pulleys. Then, calculate the belt length based on the pulley diameters and center distances. It’s always better to double-check your measurements to avoid ordering the wrong size. I once made the mistake of ordering a belt based on a rough estimate. It turned out to be too short, causing a lot of downtime and frustration. Accurate measurements are essential for a successful belt replacement.
What are the advantages of ribbed belts?
Wondering why you should choose ribbed belts over other types? Missing out on the benefits means potentially sacrificing performance and efficiency. Discover the advantages of ribbed belts for your applications.
Ribbed belts offer several advantages, including high power transmission, flexibility, heat resistance, and quiet operation. These benefits make them ideal for demanding applications requiring efficiency and reliability.
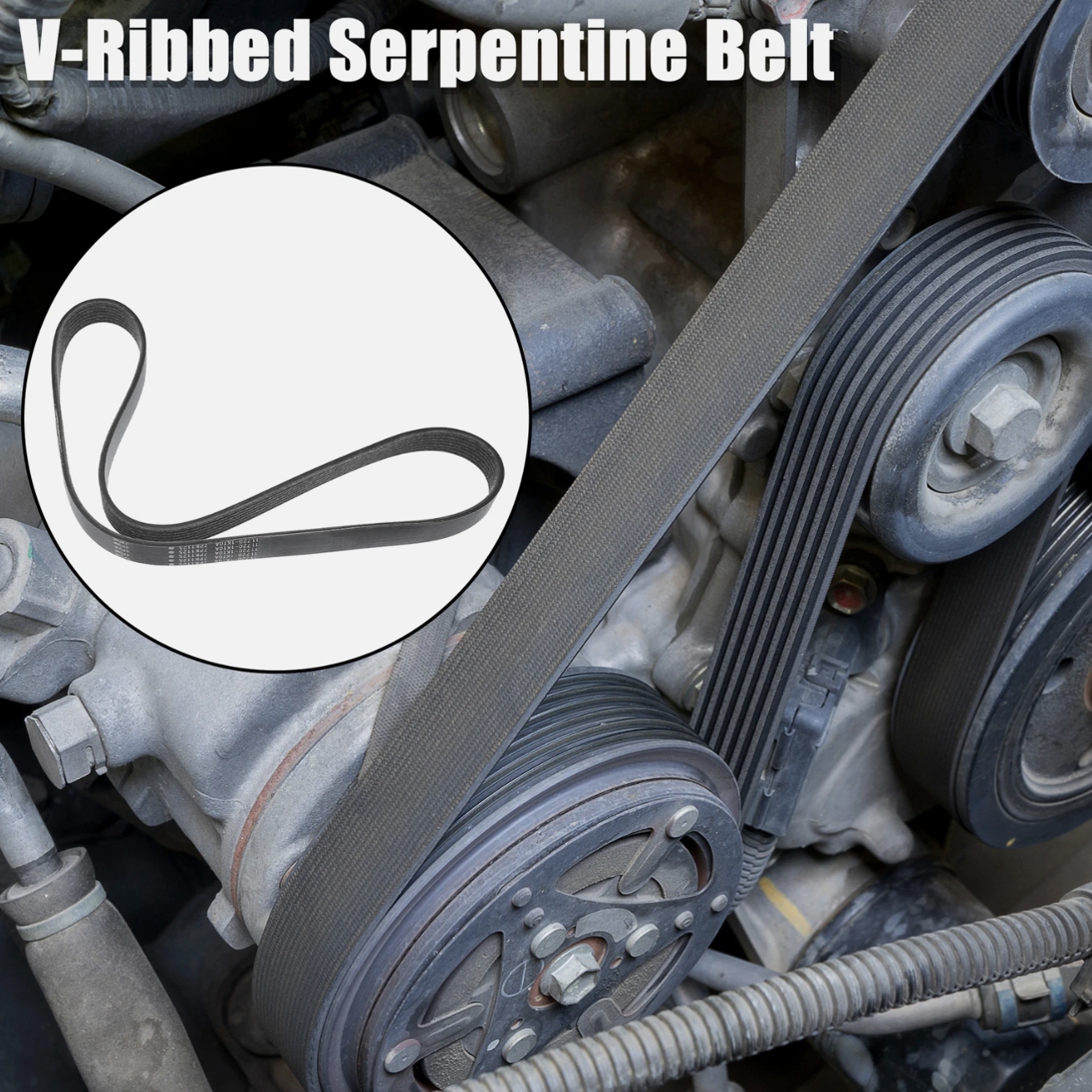
Ribbed belts have become a popular choice. They offer a unique combination of features. One of the main advantages is their high-power transmission capability. The multiple ribs provide a large contact area. This allows the belt to grip the pulleys more effectively and transmit more power. They are also very flexible, which allows them to be used with smaller pulleys. This is useful in compact engine compartments or other tight spaces. Ribbed belts generate less heat than traditional V-belts. Their design promotes better airflow, which helps dissipate heat and extends the belt’s lifespan. These belts operate more quietly than other types of belts. This is due to their smooth, continuous surface and the reduced vibration. I remember when a client switched to ribbed belts in their factory. They were amazed at how much quieter the machinery became. Another client was struggling with frequent belt failures. After switching to ribbed belts, they saw a significant improvement in belt life and reduced downtime. Ribbed belts provide a superior solution for many power transmission needs.
Conclusion
Understanding belt section designations is key to choosing the right ribbed V-belt. Correct selection ensures optimal performance. It also prevents costly downtime.
SANTE offers a diverse selection of Ribbed V-Belts in various profiles, including PK/PJ/PH/PL/PM, Double-sided Ribbed V-Belts (DPK/DPL), Elastic Ribbed/Poly V-Belts (EPK/EPJ/EPH), and Top-coated Ribbed/Poly V-Belts. Contact us to find the perfect belt for your needs.


